V2 Network Protocol
Background
Current State
The Choria V1 protocol requires x509, there is no other option.
Experience with mcollective showed that companies had little appetite to understand or use esoteric security protocols, even those based on sound industry standard cryptographic methods. Further most companies already had mature x509 infrastructure either standalone or part of systems like Puppet which made for an easy adoption path.
Choria therefor is built on a protocol that requires x509 semantics and supports nothing else:
- Every message is signed by a x509 key
- Every client-initiated message contains the x509 public key
- Servers listen on TLS using x509 public and private keys
- User identities are tied to the properties of the certificates
- User permissions and roles are tied to the identity of the certificate, very limited support for fine-grained roles
- All JWT files are signed by x509 keys
- Generally only RSA is supported
- mTLS is used to create a private network - requiring a purpose specific CA or intermediate CA in practice
- A local cache of certificates is used like a kind of safety check to catch credentials being re-issued
- Any NATS client connecting to Choria broker requires a cert/key/ca and do full mTLS
Choria supports a mode combined with the AAA Server where a user does not need her own x509 certificate but holds a JWT instead obtained from an SSO service. In this scenario the AAA Server still holds a x509 cert (called a privileged certificate) and is allowed to sign and encode requests on behalf of others (holders of a JWT) by using its x509 key pair to sign on behalf of the user.
Problem Statement
In practice this works well for most users, but those with very large or complex networks can run into problems either with corporate Certificate Authority policies or corporate CA configuration making it very hard to achieve a secure network with the facilities available. General CA infrastructure is also just getting a bit old and better alternatives exist. JWTs are now used pervasively in modern IT and the user based are more likely to accept their use for our needs.
We would like to explore, and enable, other use cases outside of server management such as IoT, purpose built backplanes, Kubernetes side cars and more, integration into Certificate Authorities in those cases is really problematic.
- x509 signatures are big and slow
- x509 certificates are also huge and these go with every request
- x509 certificate management, especially across multiple client machines is very difficult
- Dealing with short-lived (minutes) x509 certificates can be really hard
- Not all CAs have sane enrollment, some requires private keys to be copied around making them useless
- Newer technologies like ed25519 is attractive as they use small keys and signatures and can also do things like DH Key exchange
- Using ed25519 opens the possibility of using ssh keys as signing keys, something many users have requested
- Obtaining private CAs or intermediate CAs is often impossible forcing CA reuse and nullifying the usefulness of the mTLS security
- Verification of certificates happen during caching rather than a separate check, more importantly the cache is used often as a means of retrieving privileged certs and more by id
- The local cert cache is deeply embedded in the v1 protocol, but it’s proven to be useless and most people disable its enforcing features - it cannot be disabled entirely
- As Choria have evolved we need a much more granular role based permissions on each connection - can they use streams, can they admin streams, can they make rpc requests etc
- More and more servers need to be able to make request either when publishing signed registration payloads or when interacting with Choria Services from within autonomous agents. With v1 protocol this was not possible.
Solution Overview
We will support an additional protocol, while maintaining v1 protocol, that will be based on JWTs signed using ed25519 that embed their public component in the signed JWT.
We have already done the work to design and incorporate the JWTs for clients and servers at the transport level but now need to move that work into the Choria protocol so clients can communicate with Choria without x509 certificates.
Transport Security
Transport security is primarily about how the packets between Choria Broker and Choria Client/Server are secured but touches a bit on how users with access to the NATS Server are limited to just their traffic.
mTLS optional Chain of Trust for transport security
In a mTLS secured network trust is established by way of the CA signing all certificates and all parties verifying this fact. Both sides of the TLS connection will verify the other side to ensure its certificate is signed by a cached local CA chain.
This way there can be no untrusted middlemen or session hijacking in the network path.
In practice, in enterprise networks, there are many challenges:
- it’s often highly desirable to be able to hijack connections, for example to audit that PII doesn’t leave the legal jurisdiction it belongs in, many companies wish to disable the full mTLS while still maintaining strong identification of entities.
- it’s also desirable to deploy Choria Brokers using websocket protocol and offload the TLS work onto a load balancer - this would be quite complex with the current model.
- most enterprise have policies making CA rotation necessary and quite frequent, this makes mTLS completely unworkable at scale.
- dropping mTLS, or not being able to do mTLS, would impact the strength of identity since we combine the transport and identity in one cert
- certificate enrolment is done poorly, there are few protocols like ACME in use in Enterprises, often they would design their own enrollment, and mostly it involves moving keys between machines and are very slow
So we will support verified or unverified TLS to the brokers, but clients and servers all must present a signed JWT when not in mTLS mode. This will split the identity from transport security and give people the choice to pick one without compromising the other.
Servers and clients will have:
- An ed25519 seed file example
server.seedkept private and never transmitted over the network - A JWT file that holds:
- the public key of the ed25519 seed
- an identity
- a private network ID derived from the identity or seed
- Standard items like expiry times etc
- Additional permissions to control access to broker subjects
- The JWT will be signed by a trusted ed25519 key
The broker will only allow connections that holds a valid, signed JWT where the signature is made using a trusted ed25519 key.
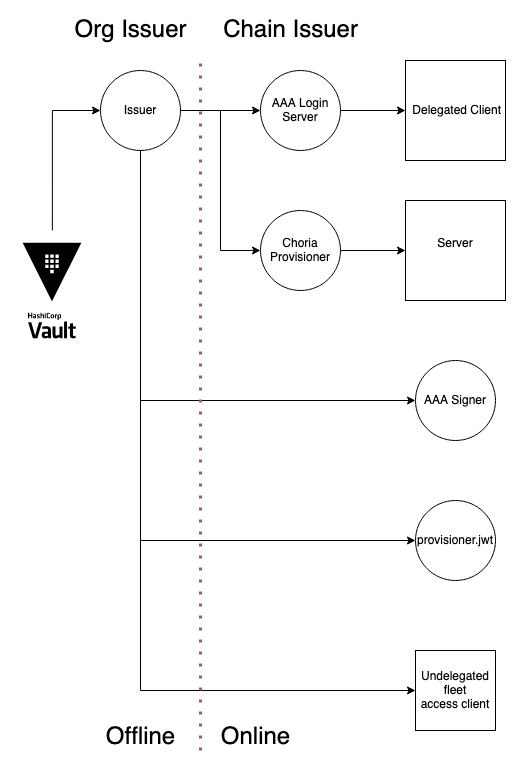
Organization and Chained Issuers
Conceptually Choria Broker can separate connections into something called “accounts” in NATS terms, for Choria we call this an Organization. Today we support just one Organization - choria - but we will look to support more in future.
We will add a concept called an Organization Issuer that is a ed25519 key that must, on a basic level, sign all tokens. To facilitate separation of concerns in our centralized AAA mode the Issuer can delegate JWT issuing in a chain to downstream issuers. The tokens will validate as being signed by the issuer essentially.
We support storing the Organization Issuer offline in something like Vault and at the “AAA Login Server” level that issuing key can also be stored in a Vault like system.
Thus, we achieve the following chain of trust:
- We know the JWT was issued by a trusted issuer
- We verify the connecting server or client has the ed25519 seed that match the JWT because the broker force a NONCE to be signed using the seed, the seed never traverse the network since the public part is embedded in the signed JWT
- The JWT tokens are therefor not bearer tokens and if they are stolen in-flight (remember no mTLS), one cannot connect with them or make any requests using them
- We have an identity that isn’t tied to the common name of a cert and so is more fluid and adaptable
- The broker should support denying all clients without JWTs
In this way we can pick full mTLS when needed or JWT+ed25519 mode when needed and even mix and match the modes.
Reply Security
Reply security is a quite difficult problem to solve since every reply would need to be individually encrypted and decrypted - unlike transport security - this is very CPU intensive, so we have never really done it at scale.
Still, its highly desirable to hide replies destined for a specific user from other users, even those with access to the broker using their own JWT tokens.
Using the callerID as key we calculate a private inbox using the hex encoded md5(callerID), we use this to construct reply subjects for all uses, even access to other subjects like the Streams API.
The broker will set up permissions ensuring that only the callerID can access replies. This way as long as there are unique callerIDs the replies from all systems are private.
We still do not encrypt the traffic in-transit (see point about PII and desired man-in-the-middle in Enterprises), but the replies are private to the user.
% sudo choria jwt client.jwt
...
Private Network ID: 7419405695a186147a0de38f7e31a509...
...
% choria req choria_util info --debug
DEBU[0000] Publishing message with reply to choria.reply.7419405695a186147a0de38f7e31a509.4e27ca6493cb4576bb78e90ea35df38c component=clientHere we can see the reply is set to match <collective>.reply.<private network id>.<request id>, the broker ensures the holder of this JWT cannot subscribe to other users replies.
To facilitate debugging users with the OrgAdmin permission, default not granted, on their tokens can view all replies.
Submission and Registration Data Security
As each server will have a ed25519 seed and a JWT embedding the public key we will support, optionally, signing Choria Submission and Registration messages. Signatures and Tokens will be included in headers.
This way should a system need to be created where the node will ask in an async manner for operations to be done against it, think host-detected issues triggering auto remediation, these messages originating from Submission will be signed.
Recipients of these messages can be certain that the message originated from a place that had access to the nodes private key.
See #1873
Identity
Identity primarily concerns Choria Requests, this is who is the one making the request for the use by AAA.
Traditionally this is extracted from the x509 certificate common name and have some dumb rules like x.choria or x.privileged.choria since x509 certificates don’t really have a strong concept of boolean permissions.
This is awful and arbitrary, in the new model callers should be whatever they like and a flag on the JWT would identify it as privileged or not (#1836).
Caller Identity
Identity would always be extracted from the JWT of the final client. In the case of the AAA Service we would need to have the ability to include the client JWT as well as the signer JWT and the signature:
- When the signer JWT isn’t set we ensure the client signed it.
- When the signer JWT is set we ensure the JWT has the right permission to sign others requests (#1836)
- The identity of the client JWT is used for the request
- We should be able to issue JWTs that can only be used in conjunction with an AAA server who signs their requests (#1840)
This would be the identity used in things like RBAC, Audit logs and more.
The broker might set the NATS user to the identity to assist with debugging.
Request Signatures
Today requests are signed by the x509/RSA key, we’d just sign it with the ed25519 seed instead. We would not support any form of server side cache.
Client JWTs will gain permissions that state they have fleet management access and, optionally, that fleet management access requires signatures.
Issuing JWT tokens
Traditionally you would use whatever your CA does for enrolling certificates and choria enroll might help you out if you’re lucky to have a system that supports that.
For others, it would be up to the user to deliver the key, cert and ca to the right locations.
Having Server enroll separate from Client enroll is good, since its conceivable that those will be done in very different places and with different auth mechanisms.
Servers
Servers would get their JWT token from the Choria Provisioner, this is supported today and that supports setting permissions and more. The Provisioner would hold a JWT that is a Chain Issuer allowing it to sign JWTs for servers.
Clients
The current AAA Server should be extended to allow client enrollment, essentially this is already supported but there is no allowance for the client seed and new behaviors. The signing request should be extended with a signature made using the seed and the service should verify it - essentially same as the NONCE in the broker.
The AAA Service would support marking a user as standalone - he can make his own requests without AAA and has his own seed - or as requiring AAA service (#1840). He might have his own seed for signing the broker NONCE but cannot make RPC requests that were not signed by AAA service.
The AAA Login handler would hold a JWT that is a Chain Issuer allow it to sign JWTs for the clients and set policies and permissions.
The choria jwt command must also be able to issue client credentials.
Non Choria clients - like lets say a random node nats client - would need to get their hands on a JWT and seed as well, and they will have to connect with that. So there will have to be a way to enroll them, probably choria jwt or choria login with their user marked as being long term valid.
A final class of client is one that needs a short-lived permission to make a very specific request. Imagine some external orchestrator wants to invoke choria req or choria kv for a particular use. Ideally this external Orchestrator would be able to issue a JWT that would allow this to happen on any unix user. In this scenario choria login should be able to take a bearer token and present that to AAA service during choria login. The bearer token would be signed by the orchestrator and trusted by the AAA, the bearer token would be very short-lived and essentially single use. It will be used to facilitate login, Choria JWT creation and more so that the unix user would still have an ed25519 seed, but the Choria Client JWT would be custom and short-lived and restricted to purpose.
Federation
The federation system allows for moving requests and replies between uncoupled networks - essentially it’s a protocol converter and gateway.
We would not in the past create federation that would cross CA boundaries as resigning all the requests and replies was impossible. With the new system the Federation Broker should be able to have a token with Authentication Delegation set and just re-sign the request en-route. This will allow it to do translation between networks and ID schemes.
Implementation
The protocol in Choria largely defines the bytes that traverse the network and couples quite tightly with the security providers for encoding, signing etc.
In the work to support v2 protocol we are also revisiting the design of the security plugins to be more generic and support non x509 key data.
Protocol
Layered protocols are used widely and bring with them a lot of flexibility in replacing some layer with another, for example: Ethernet -> IP -> TCP -> HTTP -> REST.
Choria has a similar design:
( Transport
( Secure Request or Reply
( Request or Reply
( Any bytes, often: RPC Request or Reply )
)
)
)The efforts with v2 protocol is to replace Transport, Secure and Request/Reply with a new design, still based on JSON, but with better choices internally.
Request
A request holds the actual bytes being moved around and various claims about who is making the request.
| Field | v1 | Description |
|---|---|---|
protocol | protocol | The protocol version for this request io.choria.protocol.v2.request |
message | payload | The arbitrary data contained in the request - like a RPC request - as base64 encoded bytes |
id | requestid | The unique ID for the request, logged in AAA etc |
sender | senderid | Typically the host that the request was initiated from |
caller | callerid | Who made the request in the form of kind=name |
collective | collective | Collective this request is targeted at |
agent | agent | The agent this request is targeted at |
ttl | ttl | How long this request is valid for |
time | time | The unix nano time the request was created (unix time in v1) |
filter | filter | The request filter |
Secure Request
A secure request wraps a Request, signs it and prevents any tampering with its content.
The signature - having been made with a private key - also conveys identity and confirms the claimed identity in the Request matches what cryptographic keys are held.
The main purpose of the Secure Request is to verify what can be verified about the Request and make immutable the rest. For example, we can’t exactly verify the request time and TTL, but we can prevent it from being changed by an attacker by signing it. The caller in the Request is not verified in the Request since it’s just an arbitrary string, however the Secure Request being signed using something unique to the caller, private key, confirms the information in the request.
So the end result is immutable, or at least tamper evident, metadata about a request and likewise the request payload or message.
| Field | v1 | Description |
|---|---|---|
protocol | protocol | The protocol version for this secure request io.choria.protocol.v2.secure_request |
request | message | The request held in the Secure Request as base64 bytes |
signature | signature | A signature made of the request using the ed25519 seed of the caller |
caller | pubcert | The JWT of the caller |
signer | n/a | The JWT of the delegated signer, present when the AAA server is used |
Reply
A reply is created in response from a request and holds the request id in its payload
| Field | v1 | Description |
|---|---|---|
protocol | protocol | The protocol version for this reply io.choria.protocol.v2.reply |
message | payload | The arbitrary data contained in the reply - like a RPC reply |
request | requestid | The ID of the request this reply relates to |
sender | senderid | The host sending the reply |
agent | agent | The agent the reply originates from |
time | time | The unix nano time the request was created (unix time in v1) |
Secure Reply
A secure reply wraps a Reply, signs it and prevents any tampering with its content. The hash is a fast way to test validity of the reply.
Like the Secure Request the Secure Reply wraps the Reply in a way that makes it tamper evident via signatures and hashes.
The v2 protocol includes a signature and sender JWT however in practice this is mostly not going to be used as too costly on the receiver, however might be used for registration payload verification.
Signatures add quite a bit to the payload here, as the JWT has to be sent with, so it can be disabled using plugin.security.choria.sign_replies in the new security provider.
| Field | v1 | Description |
|---|---|---|
protocol | protocol | The protocol version for this secure reply io.choria.protocol.v2.secure_reply |
reply | message | The reply held in the Secure Request as base64 bytes |
hash | hash | A sha256 of the reply |
signature | n/a | A signature made using the ed25519 seed of the sender |
sender | n/a | The JWT of the sending host |
Transport
The transport packet is the last layer that gets sent over NATS, it holds no message specific data.
| Field | v1 | Description |
|---|---|---|
protocol | protocol | The protocol version for this transport io.choria.protocol.v2.transport |
data | data | The payload to be transport, a Secure Request or Secure Reply base64 encoded |
headers | headers | Optional headers |
Headers:
| Field | v1 | Description |
|---|---|---|
reply | reply-to | A transport specific response channel for this message, used in requests |
sender | mc_sender | The host that sent this message |
trace | seen-by | A trace of host/broker pairs that the message traversed |
federation | federation | Headers to assist federation |
Federation:
| Field | v1 | Description |
|---|---|---|
request | req | The request ID a federated message belongs to |
reply | reply-to | The original reply before federation |
targets | targets | The identities who the federated message is for |
Chained Tokens Verification
We created a Chained Token system in #1900 that allows a Organization Issuer to delegate Client and Server creation to Chained Issuers.
From a usage perspective you can say tokens.ParseClientIDToken(t, pubk) where the public key is the public part of the Organization Issuer, even when the token t is signed by a Chain Issuer. The intention is to make the configuration of a chain much easier, you only have to configure the issuer for an Organization.
Additionally the expiry of the Chain Issuer is encoded in the token, if the issuer expires first the issued token is also considered expired.
The way this is achieved is with a series of claims and signatures as described here:
The Organization Issuer for an Organization is simply an ed25519 key for the moment. If that Org Issuer is just signing some client, server or provisioner nothing special is done, it’s just signing a JWT like normal.
However if the Org Issuer wants to create a token that can sign other tokens additional information is added a Clent token, it’s called the Chain Issuer:
{
"iss": "I-514969e316eb4a7146b8066feb6af5dbc05da0965ec57c9d3a7d3299d5d98fec",
"jti": "0ujsswThIGTUYm2K8FjOOfXtY1K",
"ou": "choria",
"public_key": "bd2588d3dc309d536461caa11c0d6f639e89d7a09dc43eae052f3fb32e2d8687",
"purpose": "choria_client_id",
"tcs": "3f815723734c78ceaba5fb506347565f85fe2a0334c038ba2370c7f53f35e6c7c75ed3e95b531b6049426638201c39639dbf9b711fba5d866e7e3e30be02b401"
}jtiis a unique ID for this token. It’s a kskuid, the time component must match the issued at timeissfield indicates it is signed by a Issuer with public key514969e316eb4a7146b8066feb6af5dbc05da0965ec57c9d3a7d3299d5d98fec.public_keyis the public part of the ed25519 seed for the Chain Issueraaa_chain_delegatortcsis a signature made of[chain issuer id].[chain issuer public key]using the Org Issuer private key, in other wordssig("0ujsswThIGTUYm2K8FjOOfXtY1K.bd2588d3dc309d536461caa11c0d6f639e89d7a09dc43eae052f3fb32e2d8687", orgIssuerPrik)- The Chain Issuer JWT is signed by the Organization Issuer
This way we can verify that the Chain Issuer comes from the Issuer both by verifying the signature but also we have a piece of information that cannot be changed down the line (the tcs, signed by the Org Issuer key) which we will see again later.
In code this information, signatures etc can all be added using chainIssuer.AddOrgIssuerData(issuerPrik), with this added the token chainIssuer can issue other tokens. For a possible future integration with systems like Vault we would call out to the Vault API to sign the tcs plain text and then sign the token, hence the Organization Issuer private key never needs to leave Vault.
Now when the Chain Issuer wants to issue a new Client or Server token additional information is again added:
{
"callerid": "up=rip",
"iss": "C-0ujsswThIGTUYm2K8FjOOfXtY1K.bd2588d3dc309d536461caa11c0d6f639e89d7a09dc43eae052f3fb32e2d8687",
"issexp": 1700153647,
"jti": "b2375f965abe4bfbaf131b585cf5e1a1",
"ou": "choria",
"public_key": "676d07de6721ee396754d4e4d5fa4ee2b59a6f3b8208e760ca614bc66000e740",
"purpose": "choria_client_id",
"tcs": "3f815723734c78ceaba5fb506347565f85fe2a0334c038ba2370c7f53f35e6c7c75ed3e95b531b6049426638201c39639dbf9b711fba5d866e7e3e30be02b401.a9da5f3946c1b472f1c886912bfe5559f261e4663016846e231095bd2e16a8a253657196a5c17231fb095bc3a2d1e89e1edaddcec35dd050303e5d9cda968a04"
}jtiis a unique id for this tokenissindicates a Chain Issuer with token ID (jti)0ujsswThIGTUYm2K8FjOOfXtY1Kissued this token and his public key isbd2588d3dc309d536461caa11c0d6f639e89d7a09dc43eae052f3fb32e2d8687(the one from the previous example)issexpindicates when the Chain Issuer expirestcsis made up of first creatingsigdata[client token jti].[chain issuer tcs]and then combining that[chain issuer tcs].[sig(sigdata, chainIssuerPrik)]
This way we can, given the signed Client token and the Org Issuer Public key, validate by going backwards over these claims:
- Extract the Chain Issuer
tcs,public keyandidfromissandtcs - Verify the Organization Issuer signed the
tcsof the Chain Issuer in this token, which also verifies the public key in the issuer - Verify the
tcssignature part of the Client using public key of the Chain Issuer - Verify the expiry of the Chain Issuer
General Improvements
The security plugins handle signing, encoding, extracting of IDs and validating signatures. The current security plugins are all implemented around x509.
We will make some general improvements, rename some functions and add a few bits to the interface, detail to be discovered during implementation.
- Move the API to
[]bytebased API #1844 - Remove some string orientated security apis
- Make the JWT authoritative for the secure channel name so we can stop using md5
- Develop a tool that can decode and dump/view network packets #1484
- The entire concept of the cache to be removed #1842
- Default collective when v2 is used will be
choria#1885 - Submission can sign messages #1873
- The protocol code should be instances not a singleton so each can have unique contexts and logging
- Stronger AAA interactions by signing NONCE like data in login and sign requests
- Potentially entirely remove the concept of Trusted Signers that was a mid term stop gap till this work is complete, only used by 1 users as far as we are aware